spring overcomes the coil force, or the link is in the end of the slot. This results in less vacuum break during cooler weather and more vacuum break during warmer weather.
The split choke feature operates during the last few degrees of choke thermostat rotation. The purpose is to maintain the fast idle speed long enough to keep the engine from stalling, but allow the use of choke coil which lets the choke valve open quickly. The operation of the split choke feature is controlled by a torsion spring on the intermediate choke lever shaft. As explained earlier, air pressure action on the offset choke valve tends to force the choke valve open against tension of the choke thermostatic coil. In the last few degrees of thermostatic coil opening motion, a tang on the intermediate choke lever contacts the end of the torsion spring. This keeps the fast idle cam follower lever on the last step of the fast idle cam longer to maintain fast idle until the engine is thoroughly warm. The spring works against the thermostatic coil until the coil is hot enough to pull on the intermediate choke lever and overcome the torsion spring tension. The torsion spring must be placed in the specified notch in the vacuum break mounting bracket for the application used.
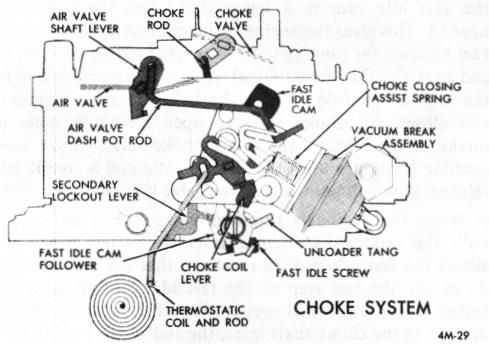
CHOKE SYSTEM (Fig. 18)
FIGURE 18
Some 4MV carburetors use a spring assist choke closing system (Figure 18). The assist spring is of the torsion type and is added to the intermediate choke shaft. It exerts pressure on the vacuum break lever to force the choke valve toward the closed choke position. The tension of the torsion spring is overcome by the choke thermostatic coil located on the engine manifold which, during the engine warmup period, will pull the choke valve open. The addition of a torsion spring assists in closing the choke valve to ensure good engine starting when the engine is cold.
Along with the choke closing assist spring, certain 4MV models use the fast idle cam "pull-off' feature.
When the engine starts and is running, manifold vacuum is applied to the vacuum break diaphragm and the diaphragm plunger moves slowly inward to open the choke valve. As the diaphragm plunger moves inward, a tang on the plunger contacts the end or "tail" of the fast idle cam to "pull-off' the cam from the high step to the lower second step setting.
A slight change in the method of vacuum break adjustment is required on these models that use the fast idle cam "pull-off" feature. (See Adjustment Procedures in the 9D-5 Section of the Delco Carburetor Parts and Service Manual 9X.)
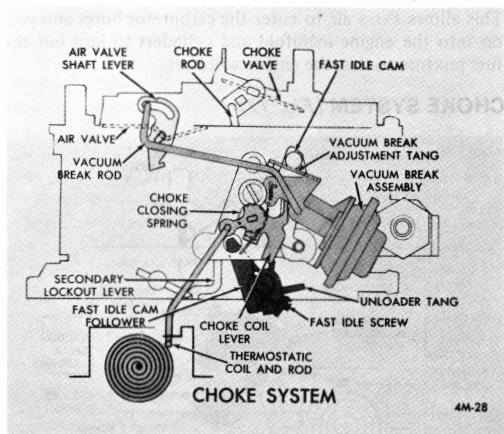
CHOKE SYSTEM (Fig. 19)
FIGURE 19
Some 4MV models have the choke closing assist spring located on the vacuum break plunger stem replacing the torsion spring located on the intermediate choke shaft.
The choke closing assist spring assists in closing the choke valve along with tension from the remote choke thermostatic coil for improved engine starting. The choke closing assist spring only exerts pressure on the vacuum break link to assist in closing the choke valve during engine starting. When the engine starts and the choke vacuum break diaphragm seats, the closing spring retainer hits a stop on the plunger stem and no longer exerts pressure on the choke valve.
The vacuum break diaphragm plunger is revised in that the slot for free travel of the air valve dashpot link is moved from the air valve shaft lever to the vacuum break plunger. A change in air valve dashpot adjustment procedure is required. (See Adjustment Procedures in the 9D-5 Section, Delco Carburetor Parts and Service Manual 9X.)