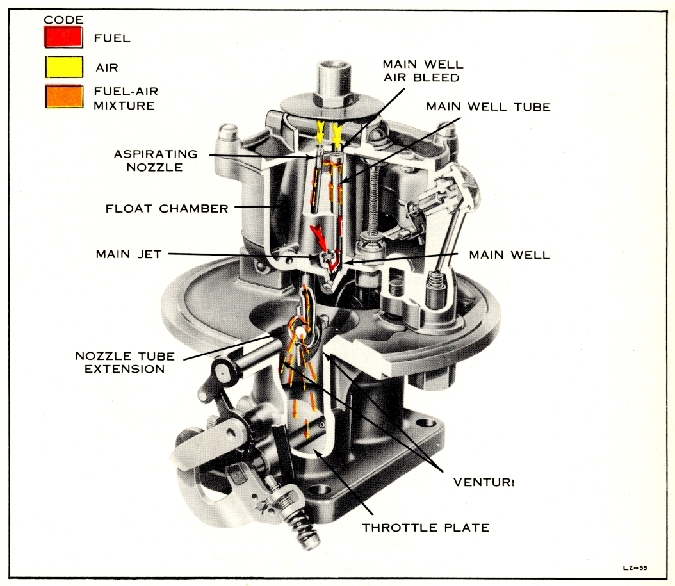
MAIN METERING SYSTEM
turn, is regulated by the speed and
power output
of the engine. The difference between
the reduced
pressure, or vacuum, in the venturi
and the normal
air pressure in the float chamber
causes fuel to
flow through the main metering system.
At cruising speed, the fuel flows
from the
float chamber through the main jet,
which meas
ures or meters the fuel, into the
bottom of the
main well. The fuel moves up the
main well and
past the narrow air bleed holes
in the side of the
main well tube. Air, which enters
the main well
tube from the main well air bleed,
is added to the
fuel by these air bleed holes. This
mixture of fuel
and air, being lighter than raw
fuel, responds faster
to any change in venturi vacuum,
and vaporizes
more readily than raw fuel when
discharged into
the air stream in the venturi. Additional
air from
the aspirating nozzle enters the
fuel as it passes
from the top of the main well to
the vertical pas
sage leading to the nozzle tube
extension. This
mixture of fuel and air is then
discharged into the
air stream in the venturi through
the drum-like
nozzle tube extension which aids
fuel distribution.
The throttle plate controls the
amount of the fuel
air mixture admitted to the intake
manifold, regu
lating the speed and power output
of the engine in
accordance with accelerator pedal
movement.
There are identical main metering
system pas
sages for both barrels of this dual
carburetor
and they function simultaneously
as described
above.
